If you're a parent worried about childhood asthma, you're not alone. As a parent myself, I know how concerning it can be when your child struggles with breathing problems.
 |
| childhood asthma |
The good news is, that asthma in children can be effectively managed with the right tools, knowledge, and action plans.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore what juvenile asthma is, how
to recognize its symptoms, and most importantly, how to help your child live an
active and healthy life despite it.
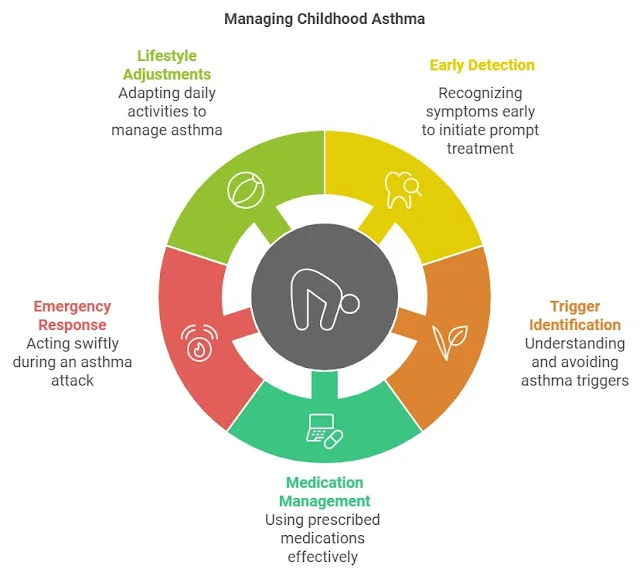
What is Childhood Asthma?
It is a chronic condition that affects the airways in your child’s lungs.
These airways become inflamed and narrow, making it hard for them to breathe.
When triggered by certain factors, asthma symptoms can worsen and make your
child feel breathless.
From my experience, asthma in youngsters can vary greatly from one child to another. Some children might experience mild symptoms, whereas others could encounter more significant challenges.
However, with the right approach,
managing childhood respiratory disorders becomes possible, helping your
child live a full and active life.
The Impact of Asthma on Children's Lives
Early Detection and Warning Signs
It’s important to catch asthma symptoms early. The sooner you identify childhood asthma symptoms, the quicker you can begin treatment. Here’s an
overview of the key points to watch for:
Common Symptoms to Watch For
- Persistent
Coughing
- This can happen,
especially at night or early in the morning.
- The cough may
worsen with cold air or exercise.
- Breathing
Changes
- You might
notice your child is breathing faster than normal.
- Shortness of
breath or chest tightness can also be signs.
- Wheezing
- Wheezing is a
whistling sound that occurs when breathing, particularly when exhaling.
- It may come
and go.
Age-Specific Symptoms
- Infants (0-2
years): Look for feeding difficulties, restless sleep, and coughing while
feeding.
- Toddlers (2-4
years): You might notice your child is less active than other kids and
tires quickly during play.
- School-age
children (5+ years): Complaints of chest tightness,
difficulty keeping up in sports, and frequent respiratory infections are
common signs.
Identifying Asthma Triggers
One of the most crucial steps in managing asthma in children is
understanding what triggers it. These triggers can be different for each child
and might include:
Environmental Triggers
- Indoor Triggers
- Dust mites in
bedding or carpets
- Pet dander
- Mould
- Strong cooking
smells or cleaning chemicals
- Outdoor
Triggers
- Pollen
- Air pollution
- Cold air
- Exercise,
especially in cold weather
Managing Environmental Factors
Making changes to your home environment can greatly reduce asthma
triggers. Here are a few methods to enhance air quality:
Bedroom Modifications
- Use
allergen-proof bedding covers
- Keep humidity
between 30-50%
- If possible,
remove the carpeting
- Make sure pets
stay out of the bedroom
Home Maintenance
- Vacuum
regularly with a HEPA filter
- Wash bedding in
hot water once a week
- Repair leaks
promptly to prevent mold growth
- Ensure ventilation throughout the home
How is Asthma Diagnosed?
Getting a proper diagnosis of juvenile asthma is crucial for
effective management. Here’s what typically happens during the diagnosis
process:
Steps in the Diagnosis Process
- Medical History
- Your child’s
doctor will ask about family history and the symptoms you’ve observed.
- Physical
Examination
- The doctor
will listen to your child's breathing and check for any signs of
allergies.
- Lung Function
Tests
- Spirometry
tests (for older children) can measure how well your child’s lungs are
working.
- Peak flow
monitoring can track breathing patterns over time.
If you’re unsure whether your child has asthma, don’t hesitate to ask for
a lung function test. It’s always cautious.
What to do in an emergency?
Asthma attacks can sometimes get severe. If your child has the following
signs, seek immediate medical attention:
- Difficulty
breathing that doesn’t improve with medication
- Trouble
speaking in full sentences
- Blue lips or
fingernails
- Chest
retractions (skin pulling in around the ribs during breathing)
Medication Options for Asthma Treatment
Managing pediatric asthma usually involves a combination of
long-term control medications and quick-relief medications.
Long-term Control Medications
These medications are taken daily to help prevent symptoms and control
inflammation:
- Inhaled
Corticosteroids
- These are
commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation in the airways.
- Leukotriene
Modifiers
- Oral
medications that help prevent asthma symptoms and improve lung function.
Quick-Relief Medications
During an asthma attack, fast-acting medications can alleviate symptoms.
- Short-acting
Beta Agonists
- These inhalers
provide immediate relief by relaxing the muscles around the airways.
Proper Inhaler Use
Learning how to use an inhaler properly is crucial. Here’s the
step-by-step process:
- Shake the
inhaler well.
- Exhale fully
before placing the inhaler in your mouth.
- Seal your lips
around the mouthpiece.
- Inhale deeply
and slowly.
- Hold your
breath for 10 seconds.
- Wait, a few
minutes before using the inhaler again if needed.
Creating an Effective Asthma Action Plan
A clear asthma action plan is essential for managing your child’s
condition. This plan should include:
- Daily
Management: This involves regular medication, avoiding triggers, and tracking
symptoms.
- Early Warning
Signs: Recognizing symptoms early can prevent an asthma attack.
- Emergency
Response: Have clear steps in case your child has a severe asthma episode,
including emergency contact information.
Living Actively with Asthma
Children with asthma need to remain active, and exercise-induced
asthma doesn’t need to prevent that. Here’s how you can help:
- Before Exercise:
- Ensure your
child warms up properly.
- Use
pre-exercise medication if prescribed.
- Always have a
rescue inhaler on hand.
- Activity
Modifications:
- Plan indoor
activities on high-pollen days.
- Choose
exercises with lower intensity if needed.
School Considerations
Kids with asthma should still be able to participate in
school activities. Here’s what you can do:
- Communication
with School Staff:
- Share your
child’s asthma action plan with teachers and staff.
- Ensure that
all school personnel know how to use your child’s medication.
- Environmental
Accommodations:
- Indoor recess
when the air quality is poor.
- Access to
medication during school hours.
Prevention Tips for Parents
In my experience, preventing asthma symptoms is just as important as
treating them. Here are some useful tips on creating a safer environment for your
child:
Home Environment Modifications
- Bedroom
Optimization:
- Use
allergen-proof covers for pillows and mattresses.
- Wash bedding
weekly in hot water.
- Keep humidity
between 30-50% to avoid mold growth.
- Air Quality
Management:
- Install HEPA
air purifiers in the bedroom.
- Open windows
when pollen counts are low.
- Avoid smoking
indoors and keep pets out of the bedroom.
Lifestyle Prevention Strategies
- Diet and
Nutrition:
- Encourage a
healthy diet, rich in anti-inflammatory foods.
- Ensure your
child stays hydrated.
- Physical
Activity:
- Encourage
regular exercise to build lung strength.
- Make sure your
child warms up properly before exercise.
- Seasonal
Considerations:
- Monitor pollen
counts in spring and summer.
- Ensure your
child is dressed warmly during the winter months.
Frequently Asked Questions About Childhood Asthma
Does Childhood Asthma Go Away?
Asthma is a lifelong condition, but it can improve with age. Certain
children might eventually "outgrow" their symptoms, whereas others
could continue to have asthma into adulthood Keep in mind that early management can
significantly improve your child’s quality of life.
How Can You Identify Asthma in a
Child?
Look for symptoms like wheezing, persistent coughing (especially at
night), chest tightness, and rapid breathing. If your child shows these signs,
it’s best to see a doctor for a diagnosis.
Is Childhood Asthma Curable?
Unfortunately, there’s no cure for asthma, but it can be managed
effectively with the right treatment plan.
How Can You Manage Childhood Asthma
Successfully?
Successful management of asthma involves:
- Consistent
medication use.
- Regular medical
check-ups.
- Identifying and
avoiding triggers.
- Following an
asthma action plan.
Conclusion
I hope this guide has helped you understand more about childhood
asthma and how to manage it. Remember, early recognition, proper treatment,
and preventive measures make a big difference. With the right approach, most
children with asthma can live an active, healthy life.
Stay in regular contact with your child’s healthcare
provider, follow their asthma action plan, and make necessary changes to the
home environment. By doing so, you’ll help ensure that your child’s asthma is
under control and their quality of life is the best it can be.